See our collection for all versions of Qwen3 including GGUF, 4-bit & 16-bit formats.
Learn to run Qwen3-2507 correctly - Read our Guide.
Unsloth Dynamic 2.0 achieves superior accuracy & outperforms other leading quants.
✨ Read our Qwen3-2507 Guide here!
- Fine-tune Qwen3 (14B) for free using our Google Colab notebook here!
- Read our Blog about Qwen3 support: unsloth.ai/blog/qwen3
- View the rest of our notebooks in our docs here.
- Run & export your fine-tuned model to Ollama, llama.cpp or HF.
| Unsloth supports | Free Notebooks | Performance | Memory use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen3 (14B) | ▶️ Start on Colab | 3x faster | 70% less |
| GRPO with Qwen3 (8B) | ▶️ Start on Colab | 3x faster | 80% less |
| Llama-3.2 (3B) | ▶️ Start on Colab | 2.4x faster | 58% less |
| Llama-3.2 (11B vision) | ▶️ Start on Colab | 2x faster | 60% less |
| Qwen2.5 (7B) | ▶️ Start on Colab | 2x faster | 60% less |
Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507

Highlights
We introduce the updated version of the Qwen3-4B non-thinking mode, named Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507, featuring the following key enhancements:
- Significant improvements in general capabilities, including instruction following, logical reasoning, text comprehension, mathematics, science, coding and tool usage.
- Substantial gains in long-tail knowledge coverage across multiple languages.
- Markedly better alignment with user preferences in subjective and open-ended tasks, enabling more helpful responses and higher-quality text generation.
- Enhanced capabilities in 256K long-context understanding.
Model Overview
Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507 has the following features:
- Type: Causal Language Models
- Training Stage: Pretraining & Post-training
- Number of Parameters: 4.0B
- Number of Paramaters (Non-Embedding): 3.6B
- Number of Layers: 36
- Number of Attention Heads (GQA): 32 for Q and 8 for KV
- Context Length: 262,144 natively.
NOTE: This model supports only non-thinking mode and does not generate <think></think> blocks in its output. Meanwhile, specifying enable_thinking=False is no longer required.
For more details, including benchmark evaluation, hardware requirements, and inference performance, please refer to our blog, GitHub, and Documentation.
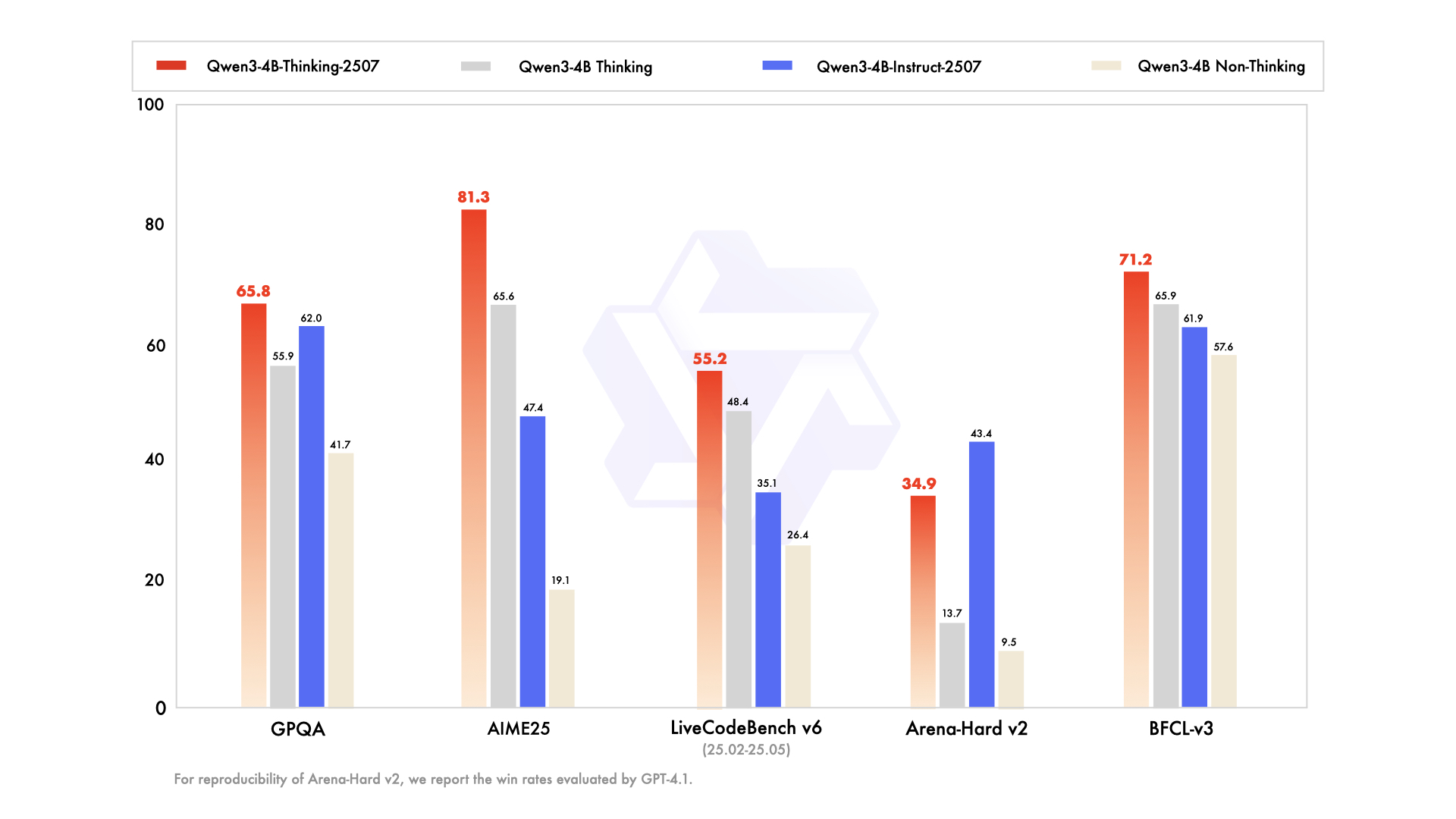
Performance
| GPT-4.1-nano-2025-04-14 | Qwen3-30B-A3B Non-Thinking | Qwen3-4B Non-Thinking | Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Knowledge | ||||
| MMLU-Pro | 62.8 | 69.1 | 58.0 | 69.6 |
| MMLU-Redux | 80.2 | 84.1 | 77.3 | 84.2 |
| GPQA | 50.3 | 54.8 | 41.7 | 62.0 |
| SuperGPQA | 32.2 | 42.2 | 32.0 | 42.8 |
| Reasoning | ||||
| AIME25 | 22.7 | 21.6 | 19.1 | 47.4 |
| HMMT25 | 9.7 | 12.0 | 12.1 | 31.0 |
| ZebraLogic | 14.8 | 33.2 | 35.2 | 80.2 |
| LiveBench 20241125 | 41.5 | 59.4 | 48.4 | 63.0 |
| Coding | ||||
| LiveCodeBench v6 (25.02-25.05) | 31.5 | 29.0 | 26.4 | 35.1 |
| MultiPL-E | 76.3 | 74.6 | 66.6 | 76.8 |
| Aider-Polyglot | 9.8 | 24.4 | 13.8 | 12.9 |
| Alignment | ||||
| IFEval | 74.5 | 83.7 | 81.2 | 83.4 |
| Arena-Hard v2* | 15.9 | 24.8 | 9.5 | 43.4 |
| Creative Writing v3 | 72.7 | 68.1 | 53.6 | 83.5 |
| WritingBench | 66.9 | 72.2 | 68.5 | 83.4 |
| Agent | ||||
| BFCL-v3 | 53.0 | 58.6 | 57.6 | 61.9 |
| TAU1-Retail | 23.5 | 38.3 | 24.3 | 48.7 |
| TAU1-Airline | 14.0 | 18.0 | 16.0 | 32.0 |
| TAU2-Retail | - | 31.6 | 28.1 | 40.4 |
| TAU2-Airline | - | 18.0 | 12.0 | 24.0 |
| TAU2-Telecom | - | 18.4 | 17.5 | 13.2 |
| Multilingualism | ||||
| MultiIF | 60.7 | 70.8 | 61.3 | 69.0 |
| MMLU-ProX | 56.2 | 65.1 | 49.6 | 61.6 |
| INCLUDE | 58.6 | 67.8 | 53.8 | 60.1 |
| PolyMATH | 15.6 | 23.3 | 16.6 | 31.1 |
*: For reproducibility, we report the win rates evaluated by GPT-4.1.
Quickstart
The code of Qwen3 has been in the latest Hugging Face transformers and we advise you to use the latest version of transformers.
With transformers<4.51.0, you will encounter the following error:
KeyError: 'qwen3'
The following contains a code snippet illustrating how to use the model generate content based on given inputs.
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_name = "Qwen/Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507"
# load the tokenizer and the model
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype="auto",
device_map="auto"
)
# prepare the model input
prompt = "Give me a short introduction to large language model."
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True,
)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# conduct text completion
generated_ids = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=16384
)
output_ids = generated_ids[0][len(model_inputs.input_ids[0]):].tolist()
content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
print("content:", content)
For deployment, you can use sglang>=0.4.6.post1 or vllm>=0.8.5 or to create an OpenAI-compatible API endpoint:
- SGLang:
python -m sglang.launch_server --model-path Qwen/Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507 --context-length 262144 - vLLM:
vllm serve Qwen/Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507 --max-model-len 262144
Note: If you encounter out-of-memory (OOM) issues, consider reducing the context length to a shorter value, such as 32,768.
For local use, applications such as Ollama, LMStudio, MLX-LM, llama.cpp, and KTransformers have also supported Qwen3.
Agentic Use
Qwen3 excels in tool calling capabilities. We recommend using Qwen-Agent to make the best use of agentic ability of Qwen3. Qwen-Agent encapsulates tool-calling templates and tool-calling parsers internally, greatly reducing coding complexity.
To define the available tools, you can use the MCP configuration file, use the integrated tool of Qwen-Agent, or integrate other tools by yourself.
from qwen_agent.agents import Assistant
# Define LLM
llm_cfg = {
'model': 'Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507',
# Use a custom endpoint compatible with OpenAI API:
'model_server': 'http://localhost:8000/v1', # api_base
'api_key': 'EMPTY',
}
# Define Tools
tools = [
{'mcpServers': { # You can specify the MCP configuration file
'time': {
'command': 'uvx',
'args': ['mcp-server-time', '--local-timezone=Asia/Shanghai']
},
"fetch": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["mcp-server-fetch"]
}
}
},
'code_interpreter', # Built-in tools
]
# Define Agent
bot = Assistant(llm=llm_cfg, function_list=tools)
# Streaming generation
messages = [{'role': 'user', 'content': 'https://qwenlm.github.io/blog/ Introduce the latest developments of Qwen'}]
for responses in bot.run(messages=messages):
pass
print(responses)
Best Practices
To achieve optimal performance, we recommend the following settings:
Sampling Parameters:
- We suggest using
Temperature=0.7,TopP=0.8,TopK=20, andMinP=0. - For supported frameworks, you can adjust the
presence_penaltyparameter between 0 and 2 to reduce endless repetitions. However, using a higher value may occasionally result in language mixing and a slight decrease in model performance.
- We suggest using
Adequate Output Length: We recommend using an output length of 16,384 tokens for most queries, which is adequate for instruct models.
Standardize Output Format: We recommend using prompts to standardize model outputs when benchmarking.
- Math Problems: Include "Please reason step by step, and put your final answer within \boxed{}." in the prompt.
- Multiple-Choice Questions: Add the following JSON structure to the prompt to standardize responses: "Please show your choice in the
answerfield with only the choice letter, e.g.,"answer": "C"."
Citation
If you find our work helpful, feel free to give us a cite.
@misc{qwen3technicalreport,
title={Qwen3 Technical Report},
author={Qwen Team},
year={2025},
eprint={2505.09388},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.09388},
}
- Downloads last month
- 67,908
1-bit
2-bit
3-bit
4-bit
5-bit
6-bit
8-bit
16-bit
Model tree for unsloth/Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507-GGUF
Base model
Qwen/Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507