Spaces:
Running
Running
| title: Detection Metrics | |
| emoji: 📈 | |
| colorFrom: green | |
| colorTo: indigo | |
| sdk: static | |
| app_file: README.md | |
| pinned: true | |
|  | |
| This project implements object detection **Average Precision** metrics using COCO style. | |
| With `Detection Metrics` you can easily compute all 12 COCO metrics given the bounding boxes output by your object detection model: | |
| ### Average Precision (AP): | |
| 1. **AP**: AP at IoU=.50:.05:.95 | |
| 2. **AP<sup>IoU=.50</sup>**: AP at IoU=.50 (similar to mAP PASCAL VOC metric) | |
| 3. **AP<sup>IoU=.75%</sup>**: AP at IoU=.75 (strict metric) | |
| ### AP Across Scales: | |
| 4. **AP<sup>small</sup>**: AP for small objects: area < 322 | |
| 5. **AP<sup>medium</sup>**: AP for medium objects: 322 < area < 962 | |
| 6. **AP<sup>large</sup>**: AP for large objects: area > 962 | |
| ### Average Recall (AR): | |
| 7. **AR<sup>max=1</sup>**: AR given 1 detection per image | |
| 8. **AR<sup>max=10</sup>**: AR given 10 detections per image | |
| 9. **AR<sup>max=100</sup>**: AR given 100 detections per image | |
| ### AR Across Scales: | |
| 10. **AR<sup>small</sup>**: AR for small objects: area < 322 | |
| 11. **AR<sup>medium</sup>**: AR for medium objects: 322 < area < 962 | |
| 12. **AR<sup>large</sup>**: AR for large objects: area > 962 | |
| ## How to use detection metrics? | |
| Basically, you just need to create your ground-truth data and prepare your evaluation loop to output the boxes, confidences and classes in the required format. Follow these steps: | |
| ### Step 1: Prepare your ground-truth dataset | |
| Convert your ground-truth annotations in JSON following the COCO format. | |
| COCO ground-truth annotations are represented in a dictionary containing 3 elements: "images", "annotations" and "categories". | |
| The snippet below shows an example of the dictionary, and you can find [here](https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-work-with-object-detection-datasets-in-coco-format-9bf4fb5848a4). | |
| ``` | |
| { | |
| "images": [ | |
| { | |
| "id": 212226, | |
| "width": 500, | |
| "height": 335 | |
| }, | |
| ... | |
| ], | |
| "annotations": [ | |
| { | |
| "id": 489885, | |
| "category_id": 1, | |
| "iscrowd": 0, | |
| "image_id": 212226, | |
| "area": 12836, | |
| "bbox": [ | |
| 235.6300048828125, # x | |
| 84.30999755859375, # y | |
| 158.08999633789062, # w | |
| 185.9499969482422 # h | |
| ] | |
| }, | |
| .... | |
| ], | |
| "categories": [ | |
| { | |
| "supercategory": "none", | |
| "id": 1, | |
| "name": "person" | |
| }, | |
| ... | |
| ] | |
| } | |
| ``` | |
| You do not need to save the JSON in disk, you can keep it in memory as a dictionary. | |
| ### Step 2: Load the object detection evaluator: | |
| Install Hugging Face's `Evaluate` module (`pip install evaluate`) to load the evaluator. More instructions [here](https://huggingface.co/docs/evaluate/installation). | |
| Load the object detection evaluator passing the JSON created on the previous step through the argument `json_gt`: | |
| `evaluator = evaluate.load("rafaelpadilla/detection_metrics", json_gt=ground_truth_annotations, iou_type="bbox")` | |
| ### Step 3: Loop through your dataset samples to obtain the predictions: | |
| ```python | |
| # Loop through your dataset | |
| for batch in dataloader_train: | |
| # Get the image(s) from the batch | |
| images = batch["images"] | |
| # Get the image ids of the image | |
| image_ids = batch["image_ids"] | |
| # Pass the image(s) to your model to obtain bounding boxes, scores and labels | |
| predictions = model.predict_boxes(images) | |
| # Pass the predictions and image id to the evaluator | |
| evaluator.add(prediction=predictions, reference=image_ids) | |
| # Call compute to obtain your results | |
| results = evaluator.compute() | |
| print(results) | |
| ``` | |
| Regardless your model's architecture, your predictions must be converted to a dictionary containing 3 fields as shown below: | |
| ```python | |
| predictions: [ | |
| { | |
| "scores": [0.55, 0.95, 0.87], | |
| "labels": [6, 1, 1], | |
| "boxes": [[100, 30, 40, 28], [40, 32, 50, 28], [128, 44, 23, 69]] | |
| }, | |
| ... | |
| ] | |
| ``` | |
| * `scores`: List or torch tensor containing the confidences of your detections. A confidence is a value between 0 and 1. | |
| * `labels`: List or torch tensor with the indexes representing the labels of your detections. | |
| * `boxes`: List or torch tensors with the detected bounding boxes in the format `x,y,w,h`. | |
| The `reference` added to the evaluator in each loop is represented by a list of dictionaries containing the image id of the image in that batch. | |
| For example, in a batch containing two images, with ids 508101 and 1853, the `reference` argument must receive `image_ids` in the following format: | |
| ```python | |
| image_ids = [ {'image_id': [508101]}, {'image_id': [1853]} ] | |
| ``` | |
| After the loop, you have to call `evaluator.compute()` to obtain your results in the format of a dictionary. The metrics can also be seen in the prompt as: | |
| ``` | |
| IoU metric: bbox | |
| Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.415 | |
| Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.613 | |
| Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.75 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.436 | |
| Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=100 ] = 0.209 | |
| Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=100 ] = 0.449 | |
| Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=100 ] = 0.601 | |
| Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets= 1 ] = 0.333 | |
| Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets= 10 ] = 0.531 | |
| Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.572 | |
| Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=100 ] = 0.321 | |
| Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=100 ] = 0.624 | |
| Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=100 ] = 0.794 | |
| ``` | |
| The scheme below illustrates how your `for` loop should look like: | |
| 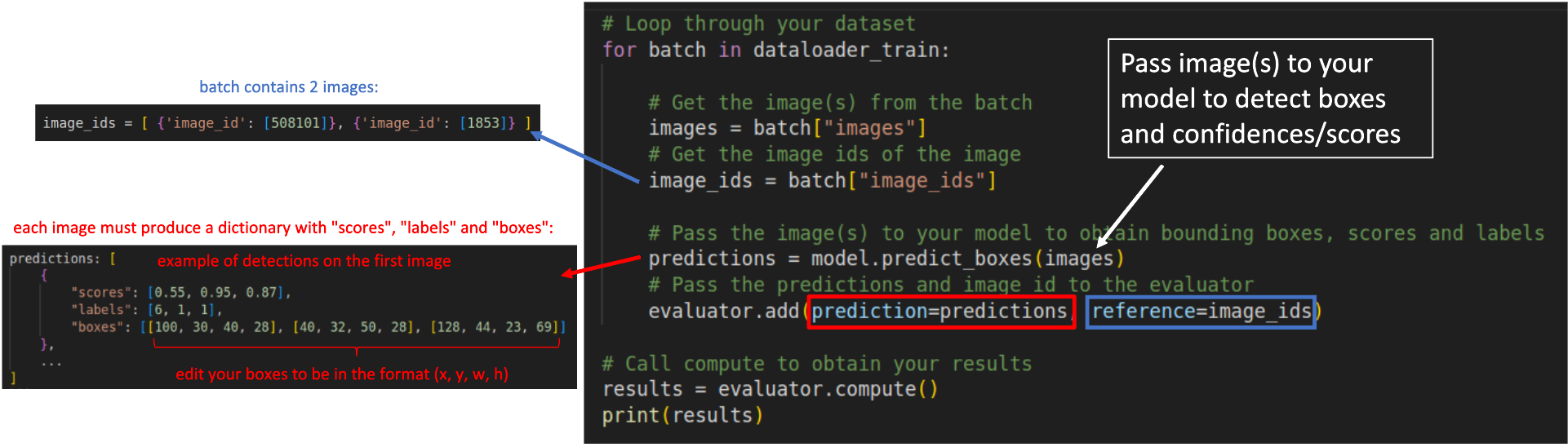 | |
| ----------------------- | |
| ## References and further readings: | |
| 1. [COCO Evaluation Metrics](https://cocodataset.org/#detection-eval) | |
| 2. [A Survey on performance metrics for object-detection algorithms](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Rafael-Padilla/publication/343194514_A_Survey_on_Performance_Metrics_for_Object-Detection_Algorithms/links/5f1b5a5e45851515ef478268/A-Survey-on-Performance-Metrics-for-Object-Detection-Algorithms.pdf) | |
| 3. [A Comparative Analysis of Object Detection Metrics with a Companion Open-Source Toolkit](https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9292/10/3/279/pdf) | |
| 4. [COCO ground-truth annotations for your datasets in JSON](https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-work-with-object-detection-datasets-in-coco-format-9bf4fb5848a4) |