license: apache-2.0
Eurus-2-7B-PRIME
Links
- 📜 Blog
- 🤗 PRIME Collection
- 🤗 RL Data
Introduction
Eurus-2-7B-PRIME is trained using PRIME (Process Reinforcement through IMplicit rEward) method, an open-source solution for online reinforcement learning (RL) with process rewards, to advance reasoning abilities of language models beyond imitation or distillation. It starts with Eurus-2-7B-SFT and trains on Eurus-2-RL-Data.

As shown in the animation above, in PRIME, the policy model and PRM are both initialized with the SFT model. For each RL iteration, the policy model first generates rollouts. Then, the implicit PRM and outcome verifier score the rollouts, and the implicit PRM gets updated on the rollouts with the outcome reward. Finally, the outcome reward and process reward are combined and used to update the policy model.
The PRIME implementation pseudocode is as follows:

The algorithm flow includes:
- Prompt filtering based on policy model performance, only preserving those on which the policy model achieves a accuracy between 0.2 and 0.8.
- Calculate implicit process reward .
- Update Implicit PRM based on predicted implicit process reward and ground truth outcome label .
- Advantage estimation with RLOO. Specifically, we first calculate the return of outcome rewards and implicit process rewards separately:
For ground truth outcome rewards, we directly adopt RLOO without any modification.
For implicit process rewards, we perform a three-step process to calculate return: (1) Use the averaged implicit process rewards to calculate the leave-one-out baseline (2) Normalize the process reward at step by subtracting the baseline; (3) Calculate the discounted return for each response.
Finally, advantage is set to the combination of both returns.
5. Update the policy using PPO loss for legit importance sampling.
Usage
We apply tailored prompts for coding and math task:
System Prompt
\nWhen tackling complex reasoning tasks, you have access to the following actions. Use them as needed to progress through your thought process.\n\n[ASSESS]\n\n[ADVANCE]\n\n[VERIFY]\n\n[SIMPLIFY]\n\n[SYNTHESIZE]\n\n[PIVOT]\n\n[OUTPUT]\n\nYou should strictly follow the format below:\n\n[ACTION NAME]\n\n# Your action step 1\n\n# Your action step 2\n\n# Your action step 3\n\n...\n\nNext action: [NEXT ACTION NAME]\n
Coding
{question} + "\n\nWrite Python code to solve the problem. Present the code in \n```python\nYour code\n```\nat the end.
Math
{question} + "\n\nPresent the answer in LaTex format: \\boxed{Your answer}"
Evaluation
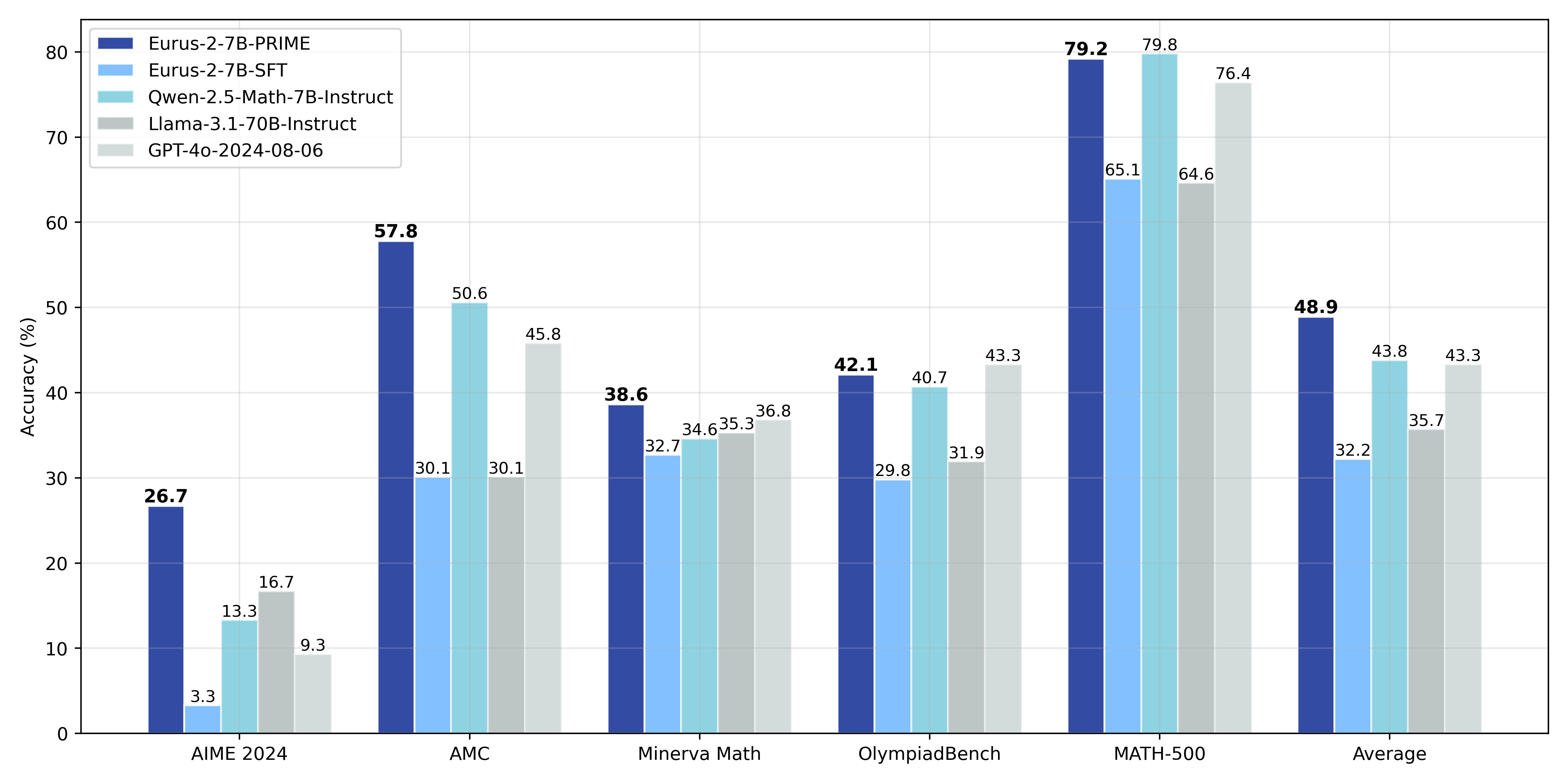
Through PRIME, we successfully achieve substantial improvements on key reasoning benchmarks over our SFT version of the model, leading to 16.7% improvement on average, and over 20% on AMC&AIME competitions. Our final model Eurus-2-7B-PRIME, based on Qwen-2.5-Math-7B-Base, surpassed its instruct version on 5 key reasoning benchmarks.
The final results are presented below:
| Eurus-2-7B-PRIME | Eurus-2-7B-SFT | Qwen-2.5-Math-7B-Instruct | Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct | GPT-4o | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIME 2024 | 26.7 (+23.3) | 3.3 | 13.3 | 16.7 | 9.3 |
| MATH-500 | 79.2 (+14.1) | 65.1 | 79.8 | 64.6 | 76.4 |
| AMC | 57.8 (+27.7) | 30.1 | 50.6 | 30.1 | 45.8 |
| Minerva Math | 38.6 (+5.9) | 32.7 | 34.6 | 35.3 | 36.8 |
| OlympiadBench | 42.1 (+12.3) | 29.8 | 40.7 | 31.9 | 43.3 |
| Avg. | 48.9 (+ 16.7) | 32.2 | 43.8 | 36.4 | 43.3 |
We achieved this with only 1/10 data and model resources compared with Qwen-Math.
| Eurus-2-7B-PRIME | Qwen2.5-Math-7B-Instruct | |
|---|---|---|
| Base Model | Qwen2.5-Math-7B | Qwen2.5-Math-7B |
| SFT Data | 230K (open-source) | 2.5M (open-source and in-house) |
| RM Data | 0 | 618K (in-house) |
| RM | Eurus-2-7B-SFT | Qwen2.5-Math-RM (72B) |
| RL Data | 150K queries 4 samples | 66K queries 32 samples |
Citation