Improve README
Browse files
README.md
CHANGED
|
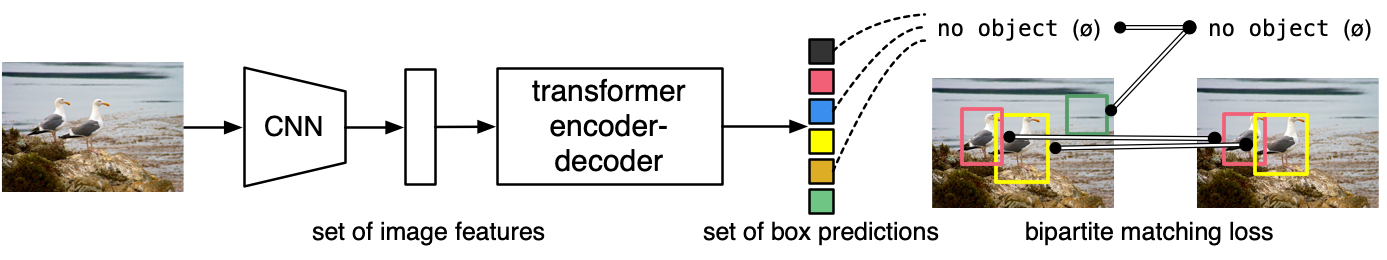
@@ -30,6 +30,8 @@ The model is trained using a "bipartite matching loss": one compares the predict
|
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
DETR can be naturally extended to perform panoptic segmentation, by adding a mask head on top of the decoder outputs.
|
| 32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 33 |
## Intended uses & limitations
|
| 34 |
|
| 35 |
You can use the raw model for panoptic segmentation. See the [model hub](https://huggingface.co/models?search=facebook/detr) to look for all available DETR models.
|
|
@@ -39,22 +41,36 @@ You can use the raw model for panoptic segmentation. See the [model hub](https:/
|
|
| 39 |
Here is how to use this model:
|
| 40 |
|
| 41 |
```python
|
| 42 |
-
|
| 43 |
-
from PIL import Image
|
| 44 |
import requests
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 45 |
|
| 46 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 47 |
image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
|
| 48 |
|
| 49 |
-
feature_extractor = DetrFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained(
|
| 50 |
-
model = DetrForSegmentation.from_pretrained(
|
| 51 |
|
|
|
|
| 52 |
inputs = feature_extractor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 53 |
outputs = model(**inputs)
|
| 54 |
-
|
| 55 |
-
|
| 56 |
-
|
| 57 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 58 |
```
|
| 59 |
|
| 60 |
Currently, both the feature extractor and model support PyTorch.
|
|
|
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
DETR can be naturally extended to perform panoptic segmentation, by adding a mask head on top of the decoder outputs.
|
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
+
|
| 34 |
+
|
| 35 |
## Intended uses & limitations
|
| 36 |
|
| 37 |
You can use the raw model for panoptic segmentation. See the [model hub](https://huggingface.co/models?search=facebook/detr) to look for all available DETR models.
|
|
|
|
| 41 |
Here is how to use this model:
|
| 42 |
|
| 43 |
```python
|
| 44 |
+
import io
|
|
|
|
| 45 |
import requests
|
| 46 |
+
from PIL import Image
|
| 47 |
+
import torch
|
| 48 |
+
import numpy
|
| 49 |
|
| 50 |
+
from transformers import DetrFeatureExtractor, DetrForSegmentation
|
| 51 |
+
from transformers.models.detr.feature_extraction_detr import rgb_to_id
|
| 52 |
+
|
| 53 |
+
url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
|
| 54 |
image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
|
| 55 |
|
| 56 |
+
feature_extractor = DetrFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained("facebook/detr-resnet-50-panoptic")
|
| 57 |
+
model = DetrForSegmentation.from_pretrained("facebook/detr-resnet-50-panoptic")
|
| 58 |
|
| 59 |
+
# prepare image for the model
|
| 60 |
inputs = feature_extractor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
# forward pass
|
| 63 |
outputs = model(**inputs)
|
| 64 |
+
|
| 65 |
+
# use the `post_process_panoptic` method of `DetrFeatureExtractor` to convert to COCO format
|
| 66 |
+
processed_sizes = torch.as_tensor(inputs["pixel_values"].shape[-2:]).unsqueeze(0)
|
| 67 |
+
result = feature_extractor.post_process_panoptic(outputs, processed_sizes)[0]
|
| 68 |
+
|
| 69 |
+
# the segmentation is stored in a special-format png
|
| 70 |
+
panoptic_seg = Image.open(io.BytesIO(result["png_string"]))
|
| 71 |
+
panoptic_seg = numpy.array(panoptic_seg, dtype=numpy.uint8)
|
| 72 |
+
# retrieve the ids corresponding to each mask
|
| 73 |
+
panoptic_seg_id = rgb_to_id(panoptic_seg)
|
| 74 |
```
|
| 75 |
|
| 76 |
Currently, both the feature extractor and model support PyTorch.
|